Shockwave-Therapy
Shockwave therapy is a multidisciplinary device used in orthopaedics, physiotherapy, sports medicine, urology and veterinary medicine. Its main assets are fast pain relief and mobility restoration. Together with being a non-surgical therapy with no need for painkillers makes it an ideal therapy to speed up recovery and cure various indications causing acute or chronic pain.
What is shockwave therapy?
Shockwave is an acoustic wave which carries high energy to painful spots and myoskeletal tissues with subacute, subchronic and chronic conditions. The energy promotes regeneration and reparative processes of the bones, tendons and other soft tissues.
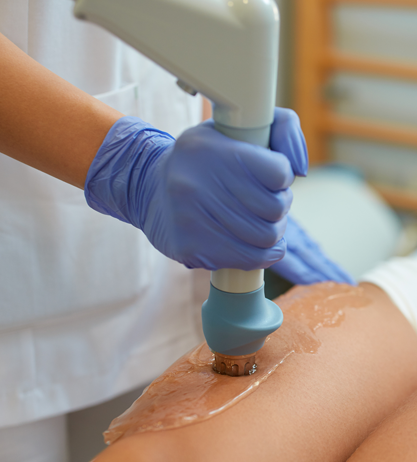
What can Shockwave Therapy help with?
- Jumper’s Knee
- Painful Shoulder
- Tennis Elbow
- Heel Spur
- Chronic Tendinopathy
- Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome
- Calcifications
- Hip Pain
Mechanism of Action
Shockwave is an acoustic wave which carries high energy to painful spots and myoskeletal tissues with subacute, subchronic and chronic conditions. The energy promotes regeneration and reparative processes of the bones, tendons and other soft tissues.
Shockwaves are characterized by jump change in pressure, high amplitude and non-periodicity.
The kinetic energy of the projectile, created by compressed air, is transferred to the transmitter at the end of the applicator and further into the tissue.
Medical Effects
Acoustic waves with high energy peak used in Shockwave therapy interact with tissue causing overall medical effects of accelerated tissue repair and cell growth, analgesia and mobility restoration. All the processes mentioned in this section are typically employed simultaneously and are used to treat chronic, sub-acute and acute (advanced users only) conditions.
-
New Blood Vessel
FormationThere may be a slight feeling of discomfort during the treatment, depending on the level of pain the patient is already experiencing in the area. However, since the treatment lasts only about five minutes, most patients are able to tolerate this discomfort.
Additionally, the intensity of the treatment can be adjusted throughout the session.
Most indications require 6-8 treatments 1-2 times per week, depending on the patient’s tolerance and their tissue response.
-
Reversal of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation occurs when the inflammatory response is not completely halted. It can damage healthy tissue and results in chronic pain. Mast cells are one of the key components of the inflammatory process. Their activity may be increased by using pervasive acoustic waves.
Mast cell activation is followed by the production of chemokines and cytokines. These pro-inflammatory compounds first enhance the inflammatory process and in the next step help restore normal healing and regenerative processes.
-
Stimulation of Collagen Production
The production of a sufficient amount of collagen is a necessary precondition for the repair processes of the damaged myoskeletal and ligamentous structures. Shockwave therapy accelerates procollagen synthesis.
The therapy forces the newly created collagen fibers into a longitudinal structure which makes the newly formed tendon fibers more dense and stiff and creates a firmer structure.
-
Dissolution of Calcified Fibroblasts
Calcium build-up is most often a result of micro-tears or other trauma to a tendon. Acoustic waves break up the existing calcifications.
Shockwave therapy starts the biochemical decalcification of the calcium build-up of a toothpaste-like consistency and treats the tendon.
The granular particles of calcium are then removed by the lymphatic system.
-
Dispersion of Pain Mediator “Substance P”
Substance P is a neurotransmitter that mediates pain information through C-fibers. This neuropeptide is generally associated with intense, persistent and chronic pain.
It relays pain messages to the central nervous system. Lowering the concentration of Substance P reduces the stimulation of afferent nociceptive fibers and thus reduces the pain.
Decreasing Substance P, histamines and other nociceptive metabolites also helps inhibit development of inflammatory oedema.
Acoustic waves generated by Shockwave therapy lower the Substance P concentration and trigger pain relief.
-
Release of Trigger
PointsTrigger points are the principal cause of pain in the back, neck, shoulder and limbs. They are associated with palpable nodules in taut bands of muscle fibers and have extremely contracted sarcomeres. The dysfunctional sarcomeres contract so tightly that they begin to cut off their own blood supply.
This causes the waste products to build up. Waste product build-up irritates the sensory nerve endings which then causes even more contraction. This vicious cycle is referred to as “metabolic crisis”.
The assumed mechanism of action is that the delivered acoustic energy unblocks the calcium pump and thus reverses the metabolic crisis in the myofilaments and releases the trigger points.
Indications
-
Jumper’s Knee
Jumper’s knee is an inflammation or injury of the patellar tendon felt as pain, tenderness and functional deficit.
This condition may interfere with or even end your patient’s sporting career regardless the age and is difficult to treat. Shockwave therapy offers simple and immediate solution.
Patient feels relief right after the first session and in several treatments the cause and the pain vanish. Scientific support Shockwave Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis
-
Painful Shoulder
Pain of the shoulder can be caused by e.g. calcifications, impingement syndrome or frozen shoulder. All the indications are a source of dull to severe pain and limit the patients in their daily life.
In calcific tendonitis of the shoulder treated by the Shockwave the calcification disappears completely in more than 85% of the cases.
Significant reduction in pain and improvement in shoulder function is observed after 4 weeks. Solution for a lot of cases is surgery or injections to which Shockwave therapy is a fitting substitute.
Scientific support Shockwave Therapy in Scapulohumeral Periarthritis with Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder
-
Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow is a frequent condition occurring in up to 10% of the general population. Unfortunately the conservative treatment of epicondylitis is lengthy (rest), includes medication (pain killers, steroid injections) and often needs repetition.
Shockwave therapy on the other hand offers a rather prompt pain relief and cure with efficiency of over 70% in just a maximum of 5 treatments.
Scientific support The Effects of Extracprporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) in Treating Lateral Epicondylitis in People Between 40 and 50 Years Old
-
Heel Spur
Calcium deposit on the underside of the heel bone (heel spur) is closely associated with scarring or inflammation of the plantar fascia (plantar fasciitis).
Either of the indications or combined, limit patients in their daily activities. Shockwave treats both of the problems simultaneously.
Acoustic waves are responsible for fast recovery, return to daily routine and long-lasting effects in up to 88% of the patients.
Scientific support Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Is Safe and Effective in the Treatment of Chronic Recalcitrant Plantar Fasciitis
-
Insertional Pain
Pain in the muscle insertions typically occurs due to repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on a particular tendon.
Through the process of neovascularization Shockwave therapy encourages more blood flow to the area and hence faster healing without the need for addictive pain medication.
Scientific support Shockwave Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy in Professional Athletes
-
Chronic Tendinopathy
Cumulated microtraumas from repetitive overloading can result in chronic tendinopathy (tendinitis or tendinosis).
Tendinopathies at various areas of the body are a widespread diagnosis of both the active persons and the general population.
Both inflammation of the tendon and damage on the cellular level are successfully treated with Shockwave.
The number of sessions is typically 3–5 with 5–10 days in-between sessions.
Scientific support Extracorporeal Radial Shockwave Therapy for the Treatment of Achilles Tendinopathies
-
Medial Tibial Stress
Medial tibial stress syndrome typically occurs due to activities placing large amounts of stress through the tibialis anterior muscle.
These activities may include fast walking or running (especially up or downhill or on hard or uneven surfaces) or sporting activity (such as kicking sports).
Patient is usually restricted from such activities for prolonged periods of time. When treated with Shockwave therapy the passive period is significantly shorter and the recovery time cuts back by at least a half.
Scientific support Low-Energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy as a Treatment for Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome
-
Calcifications
Calcifying tendinitis is a chronic painful disorder that is characterized by calcifications in rotator cuff tendons.
Such condition causes pain and range of motion limitations. Shockwave therapy is one of the most effective treatments of calcifications.
Acoustic waves cause disruption of the calcified entities and support their resorption and elimination by the body.
SWT significantly decreases treatment length and offers fast relief in chronic stages.
Scientific support Shockwave Therapy in Scapulohumeral Periarthritis with Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder
-
Hip Pain
With age and use, the cartilage can wear down or become damaged. Muscles and tendons in the hip can get overused.
The hip bone itself can be fractured during a fall or other injury. Any of these conditions can lead to pain and damage in the hip area.
Shockwave therapy enhances the healing process, fights inflammation, eliminates the pain and tenderness and can prevent hip replacement surgery.
In 79% of patients with necrosis Shockwave therapy also improves osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Scientific support Low-Energy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy as a Treatment for Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome.
FAQ
Will Shockwave therapy help me?
Most patients with chronic pain problems have been through various unsuccessful types of treatments. Up to 80% of the same patients worldwide report that Shockwave therapy has helped them eliminate their problem.
Does the treatment hurt?
There may be a slight feeling of discomfort during the treatment, depending on the level of pain the patient is already experiencing in the area. However, since the treatment lasts only about five minutes, most patients are able to tolerate this discomfort. Additionally, the intensity of the treatment can be adjusted throughout the session.
How many treatments will I need?
The number of treatments varies depending on the indication and tissue response. The effect of the treatment is cumulative, so you will typically need more than one (3–5) treatment. Very often though, you will experience relief right after the first treatment.
How often will I need the treatment?
Most indications require 6-8 treatments 1-2 times per week, depending on the patient’s tolerance and their tissue response.
Will I feel any pain after the treatment?
Most patients will experience an immediate pain relief following the treatment. However, within 2–4 hours after the treatment, they may experience some soreness in the treated area. This soreness has been reported as tolerable and not limiting.
Are there any restrictions after the treatment?
It is recommended that patients refrain from physical activity, especially one that would involve the treated region, for about 48 hours following each treatment session.
There may be a slight feeling of discomfort during the treatment, depending on the level of pain the patient is already experiencing in the area. However, since the treatment lasts only about five minutes, most patients are able to tolerate this discomfort. Additionally, the intensity of the treatment can be adjusted throughout the session.
How many treatments will I need?
The number of treatments varies depending on the indication and tissue response. The effect of the treatment is cumulative, so you will typically need more than one (3–5) treatment. Very often though, you will experience relief right after the first treatment.
How often will I need the treatment?
Most indications require 6-8 treatments 1-2 times per week, depending on the patient’s tolerance and their tissue response.
Will I feel any pain after the treatment?
Most patients will experience an immediate pain relief following the treatment. However, within 2–4 hours after the treatment, they may experience some soreness in the treated area. This soreness has been reported as tolerable and not limiting.
Are there any restrictions after the treatment?
It is recommended that patients refrain from physical activity, especially one that would involve the treated region, for about 48 hours following each treatment session.
Most indications require 6-8 treatments 1-2 times per week, depending on the patient’s tolerance and their tissue response.
Will I feel any pain after the treatment?
Most patients will experience an immediate pain relief following the treatment. However, within 2–4 hours after the treatment, they may experience some soreness in the treated area. This soreness has been reported as tolerable and not limiting.
Are there any restrictions after the treatment?
It is recommended that patients refrain from physical activity, especially one that would involve the treated region, for about 48 hours following each treatment session.
It is recommended that patients refrain from physical activity, especially one that would involve the treated region, for about 48 hours following each treatment session.